The concept of “AV over IP” has been around for longer than most people realize. Unfortunately, many folks haven’t even heard of the idea of using your home or business network as a means of transporting Audio, High Definition and even up to 4K/HDR video resolution signals.
If you’re still reading, you’re probably one of those folks. That’s fine because you’re in the right place. We’re going to enlighten you on how easy all this AV over IP stuff works and why you should not ignore this present and ever-growing technology. Our guys at BZBtv also made a video to illustrate what AV over IP is all about if you don’t feel like reading further.
What is AV over IP?
You may have heard of Video over IP, HDMI over IP, or Networked AV. It all means the same thing. Technically, AV over IP stands for “Audio-Visual over Internet Protocol”. All this is saying is you can transmit and switch audio-visual data and control signals, over a standard Ethernet network such as a LAN or the internet.
The adoption of this technology is snowballing within the AV and IT industry. Thanks to the advancements of recent AV hardware, sending AV streams over IP switches is now easier than ever.
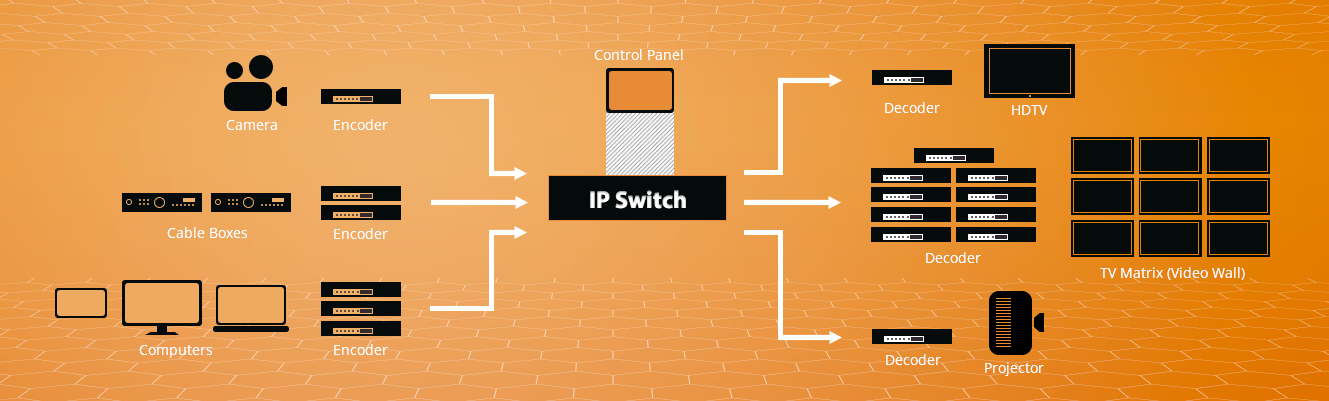
In AV over IP, the AV transmitters become encoders and the AV receivers become decoders. The AV matrix switcher becomes a standard IP switch, similar to what your computers connect to in the office.
Why Is AV over IP Better Than The Alternative?
Answering this question means understanding the technology currently used in AV infrastructures. The products found in AV spaces are designed to preserve the max image resolutions, frame rates, sound quality, and an easy to use control system with a user interface that is friendly on the eyes.
In many cases, all these products are from different manufacturers which pose a new issue, and that’s integrating and making them all communicate with each other. For example, you may be dealing with various signals such as DVI, VGA, HDMI, DisplayPort and more.
The types of products in these systems can be matrix switchers, AV scalers, video walls, multiviewers, and extenders using HDBaseT technology. Typically, these are point-to-point systems with transmitters at source devices and receivers at destination devices.

Disadvantages of Current AV Infrastructures
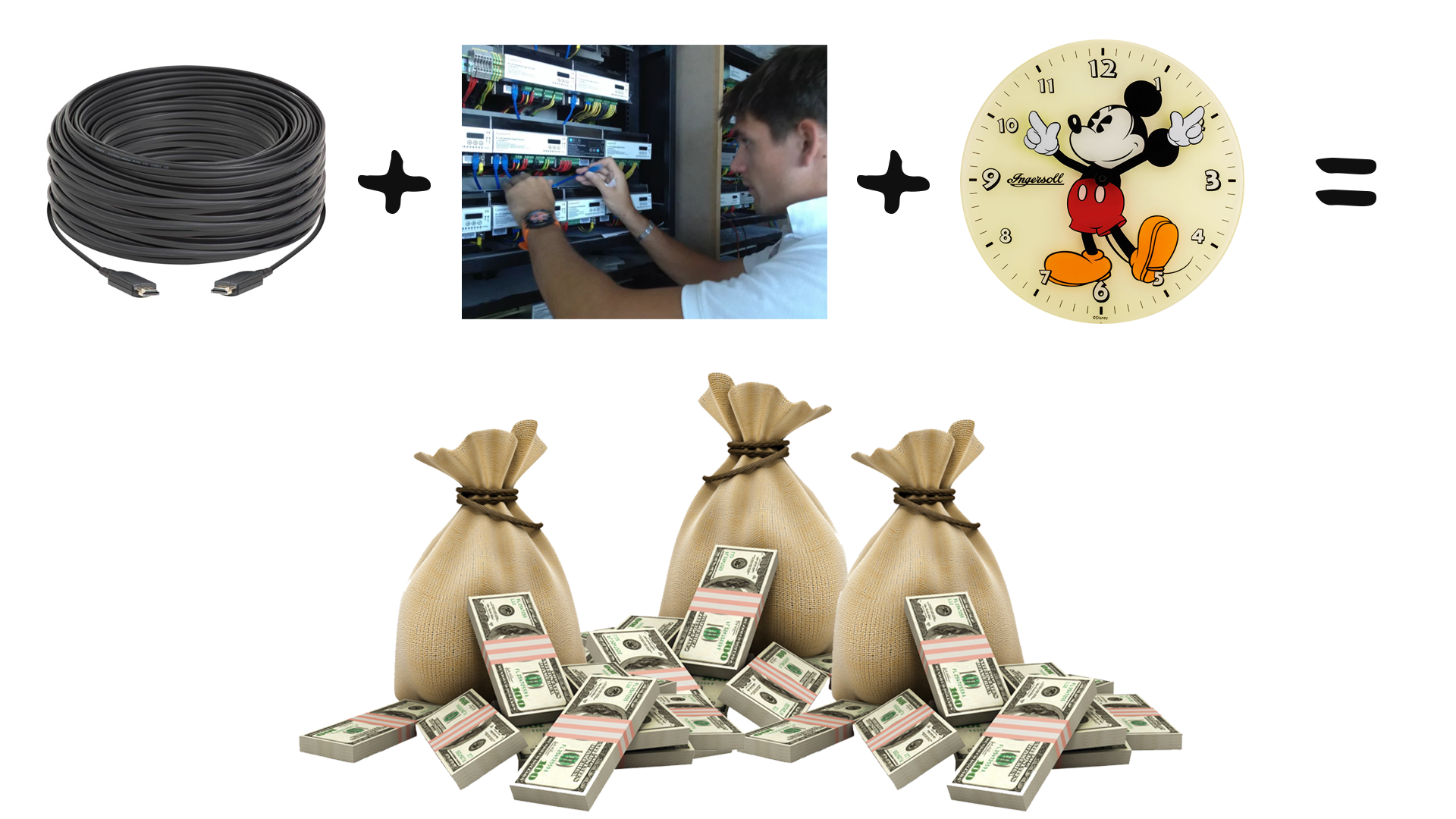
A typical matrix switch solution is a closed/separate AV network. In many cases, you’ll need to run additional cabling at long lengths. You’ll need a certified professional with specialized training to install source devices to a matrix switcher routing to multiple displays.
The labor can be expensive to run cables, not to mention the price of the cabling. Programming can be complex, especially when setting up with a 3rd party control system, equating to time and money.

Also, some equipment is limited to what a vendor has to offer which gives you zero flexibility. The result may feel complete, but with huge limitations including a restriction on capacity, such as available I/O’s.
As an AV enthusiast, you know the feeling of wanting to add one more device to your system. Although limited in some respects, these point-to-point applications offer a bandwidth-controlled environment with performance elements that include fast switching, low latency, scaling resolutions from 1080p to 4K, and changing the video signal from one type to another such as VGA to HDMI.
Advantages of AV over IP
Implementing AV over IP preserves everything about a traditional AV system. The main difference is the video and audio traveling through the series of AV components and cables shifts from circuit-based to packet-based—like computer data networks.
Instead of placing transmitters and receivers at all the devices in the room, the AV over IP design calls for an encoder at each source device like game consoles or Blu-ray players and a decoder at each destination device like TVs or projectors.

The encoders and decoders connect to Gigabit Ethernet switch/es. As a result, an application is no longer limited to a finite number of inputs and outputs. Theoretically, you can connect as many encoders, decoders, and IP switches your network design allows. Additionally, the ability to scale up comes at much lower costs.
AV over IP technology organizes the audio-visual data whether you are sending HDMI, Displayport, Thunderbolt, VGA, or control signals.
Advantages of an AV over IP system also include a single platform for AV. The number of source devices is no longer limited when physical ports run out; multiple IP switches can be connected to expand. It’s flexible breaking the distance barriers an AV system is limited to while offering a better ratio of I/O’s.
As technology advances into the future, an AV over IP system has the flexibility to scale up while keeping costs down by just adding encoders, decoders, or IP switches to the existing network. Relatively simple for anyone with essential network experience.
Why is AV over IP future technology?
AV over IP is the fastest growing technology in the AV industry. The convergence of AV and IT opens a new realm of possibilities for technology to advance. The AV over IP design differs from existing AV systems in that it’s essentially a streaming structure.
Gradually in time, the replacement of analog AV facilities with IP-based infrastructures will increase. For smaller systems, analog AV will probably remain the preferred choice for the time being.
However for larger systems requiring high-bandwidth, long distance, or even just planning for future expansion, AV-over-IP is the best solution. There is no doubt AV-over-IP is the future of AV system transmission and control. Don’t forget to visit our online store for the latest AV over IP solutions.

 BZBtv
BZBtv DIY
DIY TECH TRENDS
TECH TRENDS


